Neuroscientists have reportedly discovered a new, mysterious kind of human brain cell.
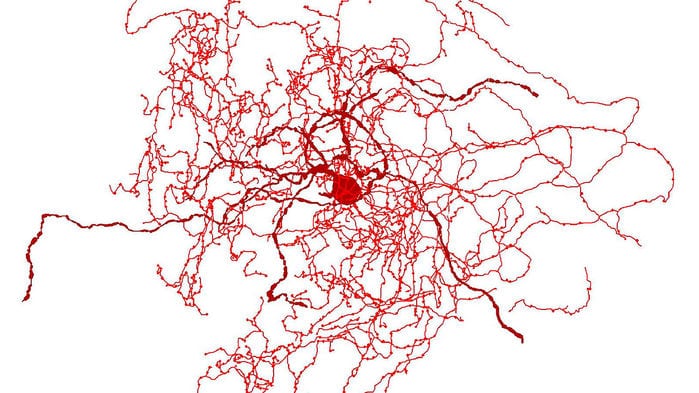
A new kind of human brain cell was found by an international group of researchers and has been called “rosehip neuron” because of its bushy appearance. What captures the interest of scientists is the fact that the neuron appears to be absent in mice and other animals used to model the human brain. At the moment, it’s only known to exist in humans.
“It’s very bushy, very compact with lots of branch points, so it kind of looks a little bit like a rosehip,” Trygve Bakken, one of the lead authors of the study published in the journal Nature Neuroscience, said in an interview.
The new brain cell was said to be responsible for silencing other neurons. Aside from that, it has not been described before. Researchers from the Allen Institute for Brain Science in Seattle and the University of Szeged in Hungary have independently identified the neurons. However, when they learned that they’re looking at the same thing, they decided to work together.
Read More: New Research on the Role of Neurons Force us to Relearn the way we Learn
According to Bakken, the rosehip neurons are inhibitory neurons that form synapses with pyramidal neurons. The latter is the primary type of excitatory neuron found in the prefrontal cortex.
“We all have inhibitory neurons and excitatory neurons, but this particular type of inhibitory neuron is what’s new in this study. It’s special based on its shape and its connections and also the genes that it expresses,” Bakken went on to explain.
“It has these really discrete connections with [pyramidal] neurons. It has the potential to sort of manipulate the circuit in a really targeted way, but how that influences behavior will have to come in later work.”
Bakken and his team were able to identify the rosehip neurons by examining the brain samples taken from two dead males in their 50s who donated their bodies to science. The samples were from the neocortex, the portion of the brain responsible for higher-order thinking.
The discovery of the rosehip neurons could potentially help explain why many experimental treatments for brain disorders conducted in mice worked but not in humans. Aside from that, it could also give scientists clues to curing brain disorders like autism and Alzheimer’s disease.
“It may be that in order to fully understand psychiatric disorders, we need to get access to these special types of neurons that exist only in humans,” Joshua Gordon, director of the National Institute of Mental Health, said.




Comments (0)
Most Recent