Lightwave computing, a new computational method, could be the breakthrough the quantum computing field has been waiting for.
The functioning of current computers and electronics is based on the movement and energy states of electrons.
The network of silicon transistors allows the motion of electrons through the application of electrical charges.
In general, the rate at which these devices apply electrical voltages is dependent on the number of transistors. This is largely dependent on the size of these microscopic on/off switches.
The smaller the switches, the higher the clock rates, and the more high-performance the computing system.
Lightwave Computing: Three Shots With one “Light Pulse”
For several decades, the main approach toward fast computing devices was the aggressive miniaturization of electronic components.
We’re already seeing the end of the miniaturization one-way tunnel.
We’ve reported about new technologies – like valleytronics and neuromorphic engineering – which seek to prolong the life of Moore’s Law as much as possible.
Now, however, a new concept promises to control the motion of electrons much faster: lightwave computing. This new method brings a lot more promise for the life of Moore’s Law.
What’s more, the technique makes the possibility of room-temperature quantum computing more likely than ever.
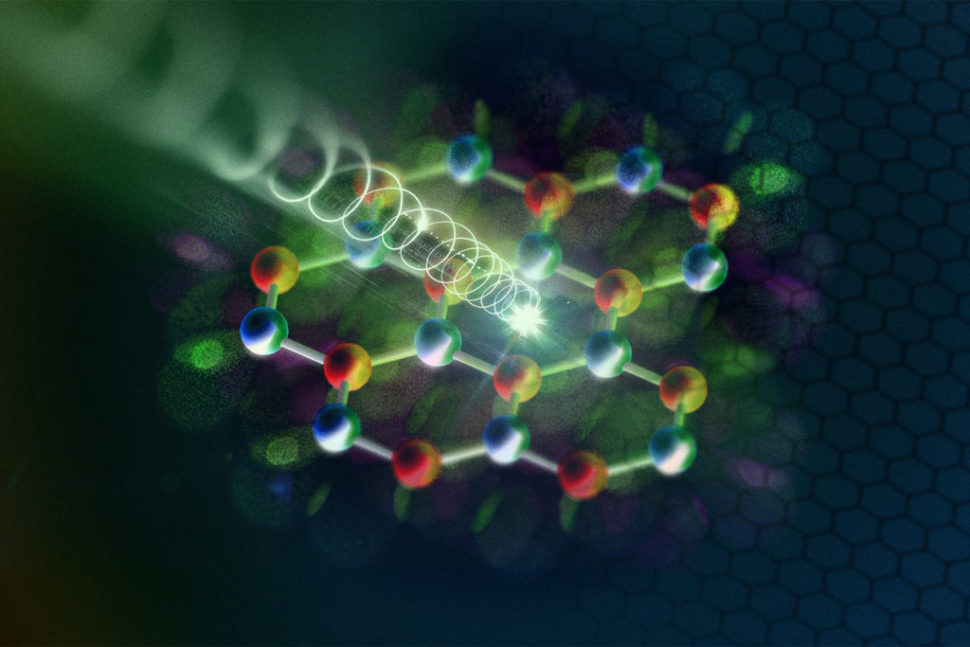
An international team of physicists from the University of Michigan, and two universities in Germany (Regensburg and Marburgin) have found a way to control the movement of electrons using electric fields generated by infrared light waves.
Researchers demonstrated how extremely short pulses of light could enable them to manipulate the motion of electrons on ultra-short timescales.
This technique, which they call lightwave computing, would allow them to control electrical currents running through the conventional transistor networks up to a million times faster.
“Ordinary electronics are in the range of gigahertz, one billion operations per second,” said U-M’s Mackillo Kira, one of the experiment lead researchers. “This method is a million times faster.”
Lightwave Computers That Verge on Quantum Territory
What the team accomplished here is nothing less than a breakthrough in valleytronics that, at the same time, allows an approach to quantum computing in a new and more convenient way.
Unlike conventional computers, quantum computing relies on qubits to encode information. It is the quantum phenomenon of superposition that allows the qubits to take two quantum states simultaneously.
At present, qubits are difficult to produce and manipulate because quantum states are extremely brief and fragile. These means they need an isolated environment where temperatures hover around absolute zero.
Scientists have been seeking to maintain qubits in a state of superposition for a sustainable duration, but this has proven to be a tough challenge.
Instead, the present experiment takes another approach by trying to act faster, before qubits lose their superposition state.
The team had to figure out how to control the change from one energy state to the other.
They achieved this by using ultra-short infrared light pulses in the femtosecond range to excite electrons and coax them into two “valleys” (two energy states) at once.
This way, there’s no need to cool qubits down to extremely low temperatures.
“In the long run, we see a realistic chance of introducing quantum information devices that perform operations faster than a single oscillation of a lightwave. The material is relatively easy to make, it works in room temperature air, and at just a few atoms thick, it is maximally compact,” said researchers.
The team calls their concept “lightwave computing” on which they published a paper titled “Lightwave valleytronics in a monolayer of tungsten diselenide”.

















Comments (0)
Most Recent