Google’s hardware day is over, and one thing that you might have missed from the event is that Google Assistant sounded more like a human than a robot now–all thanks to WaveNet!
Yesterday, Google unveiled its latest devices, led by the much-awaited Pixel 2 and Pixel 2 XL. If you were not able to witness the event, we have you covered here.
However, one thing that set the internet abuzz was that Google Assistant’s voice had been enhanced by WaveNet to sound more human-like.
For years, tech companies are not just fighting for mobile AI supremacy; they are also competing to develop the best voice-powered technology. And, Google just steps up its game by ensuring that its voice technology would produce realistic human-like voices.
#WaveNet neural network now gives Google Assistant more human-like voice!Click To TweetThat won’t be possible without Deepmind‘s deep neural network for generating raw audio, the WaveNet.

DeepMind: Acquisition and AI Works
In 2014, the London-based artificial intelligence company, DeepMind Technologies Limited was acquired by Google. The company formed the artificial intelligence research group of now Google’s parent company, Alphabet.
Back then, DeepMind was engaged in the creation of a neural network that’s capable of learning and playing video games in a manner pretty much similar to humans.
Aside from that, the company was also working on a Neural Turing machine, another neural network that could access external memory like a conventional Turing machine. This led to the development of a computer that mimics the short-term memory of a human brain.
But, one creation that made DeepMind famous was the AlphaGo, a small AI program specially created to learn and play the board game Go. So, what’s unique with this AI?
Well, AlphaGo was the first artificial intelligence program to actually beat a professional Go player WITHOUT HANDICAPS on a full-sized 19×19 board. It beat Lee Sedol, a South Korean professional Go player of 9 DAN RANK in a 1-4 series in March 2016. To celebrate the AI’s victory, it was awarded by the Korea Baduk Association with an honorary 9 Dan.
WaveNet: Google’s Hidden Weapon in Making Google Assistant Superior
Apparently, DeepMind has more in store for us. In September 2016, following the famous AlphaGo stint, the company released a paper outlining a technique for generating raw audio using a deep neural network.
The deep generative model of the raw waveforms was dubbed as WaveNet. According to a blog published by DeepMind, they spent the last 12 months working on significantly improving both the speed and quality of their model. Now, the updated version of the WaveNet is being used by Google to generate the Google Assistant voices for U.S. English and Japanese across all platforms.
The Google Assistant upgrade is viewed by many as a wise shift since Apple just released the upgraded version of its Siri virtual assistant two weeks ago.
US English Third-Party Voice
Japanese Voice
WaveNet was built using a ‘convolutional neural network‘ which was trained by the researchers on a large dataset of speech samples. The DeepMind researchers wrote:
“During this training phase, the network determined the underlying structure of the speech, such as which tones followed each other and what waveforms were realistic (and which were not). The trained network then synthesized a voice one sample at a time, with each generated sample taking into account the properties of the previous sample. The resulting voice contained natural intonation and other features such as lip smacks.
Its “accent” depended on the voices it had trained on, opening up the possibility of creating any number of unique voices from blended datasets. As with all text-to-speech systems, WaveNet used a text input to tell it which words it should generate in response to a query.”
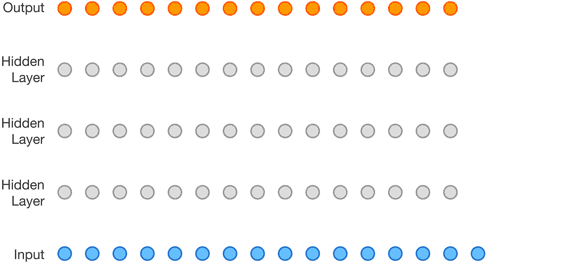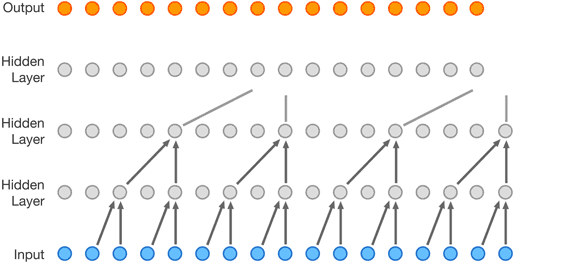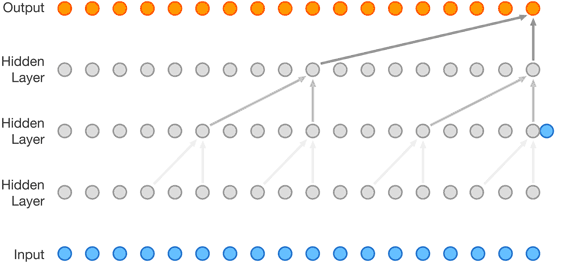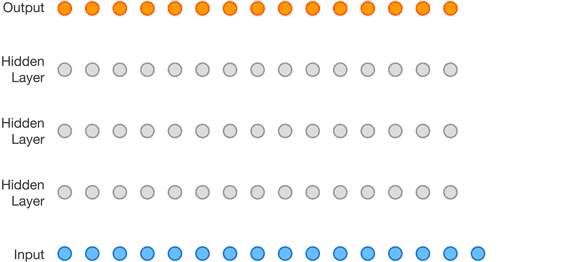
The original WaveNet model that was introduced a year ago was said to be computationally expensive, making it impossible to be deployed in the real world. So, for the past 12 months, the company worked on developing the new model that now has the capability of generating waveforms more quickly.
In addition to that, the upgraded model is capable of running at scale and is the first product to launch on Google’s latest tensor processing unit (TPU) cloud infrastructure, the company’s second-generation AI chip.
The enhanced WaveNet generated raw waveforms at speeds 1,000 times faster than the original model. That gives the said neural network just 50 milliseconds to create one second of speech.

Furthermore, the latest model also has higher-fidelity than the original one. It is capable of creating waveforms with 24,000 samples a second. Also, DeepMind researchers increased the resolution of each sample from 8 bits to 16 bits, the same resolution found on compact discs today.
“The new model also retains the flexibility of the original WaveNet, allowing us to make better use of large amounts of data during the training phase. Specifically, we can train the network using data from multiple voices. This can then be used to generate high-quality, nuanced voices even where there is little training data available for the desired output voice,” DeepMind researchers added.
Right now, DeepMind believes that WaveNet would open the door to other potential benefits that the power of voice interface could unlock.



















Comments (0)
Most Recent